A financial institution is an entity whose main economic function is to channel or help channel funds from entities with savings to entities that need funds.
In the euro area, banks are the main financial institution. Their business consists of receiving deposits or other reimbursable funds from the public and investing those funds at their own risk, for example, by granting credit or by purchasing debt securities issued by other entities. However, banks are not the only financial institution.
Which entities are classified as financial institutions?
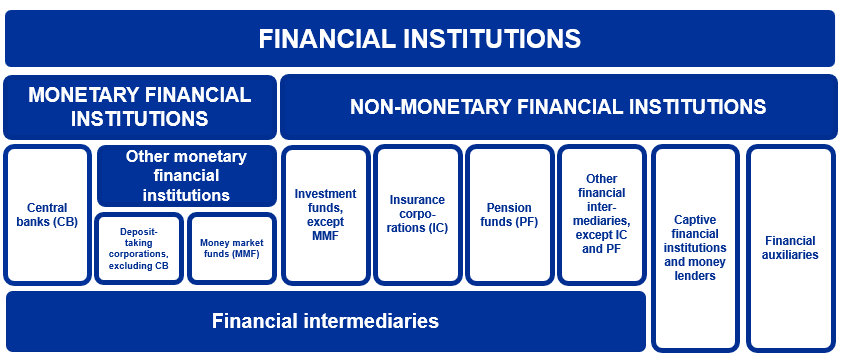
The economic sector comprising financial institutions can be divided into nine subsectors, depending on the business they carry out, the risks they take, and the type and liquidity of their liabilities.
What is the difference between monetary financial institutions and non-monetary financial institutions?
Financial institutions can be classified as monetary financial institutions (MFIs) or non-monetary financial institutions (non-MFIs), depending on their role in money creation.
MFIs are financial institutions that receive deposits or close substitutes for deposits. They are able to create money. The MFI sector is composed of central banks, deposit-taking institutions other than central banks (commonly referred to as “banks”) and money market funds (MMFs).
Non-MFIs are financial entities that are not allowed to receive deposits and, therefore, do not have the ability to create money. The non-MFI sector includes a range of institutions such as investment funds (excluding MMFs), insurance corporations, pension funds, other financial intermediaries, financial auxiliaries, captive financial institutions, and money lenders.
What are financial intermediaries ?
Financial institutions can also be categorised according to their involvement in financial intermediation. Financial intermediaries are entities which, during the financial intermediation process, take on risks on their own account by purchasing financial assets and incurring debts/liabilities with the general public. Financial intermediaries include banks, investment funds, insurance corporations and pension funds.
Financial auxiliaries are not exposed to risks when taking on assets and liabilities – they act solely on behalf of their customers and facilitate financial intermediation. Financial auxiliaries include entities that manage the wealth of third parties but do not invest on their own account, such as wealth management companies and investment fund management companies, and entities that help with intermediation, such as insurance brokers.
Captive financial institutions and money lenders neither engage in financial intermediation nor provide ancillary services. They may hold shares or participating interests in a group of subsidiaries but do not provide any other services to them.
Related explainers
What is a monetary financial institution?
What is a non-monetary financial institution?